Configuring the Apache server path on AlmaLinux is a crucial step in setting up a web server. AlmaLinux, a binary-compatible fork of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), offers a stable and secure platform for hosting websites and web applications. Apache, being one of the most popular web servers, is widely used for its flexibility and scalability. In this article, we will explore five ways to configure the Apache server path on AlmaLinux, providing a comprehensive guide for system administrators and web developers.
Key Points
- Understanding the default Apache server path configuration on AlmaLinux
- Configuring the Apache document root
- Setting up virtual hosts for multiple websites
- Configuring Apache server paths for SSL/TLS encryption
- Optimizing Apache server performance through path configuration
Understanding Default Apache Configuration

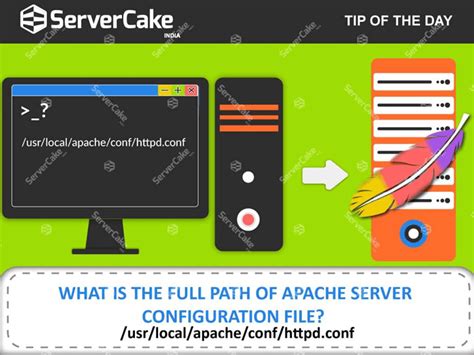
Before diving into custom configurations, it’s essential to understand the default Apache setup on AlmaLinux. By default, Apache stores its configuration files in /etc/httpd/, with the main configuration file being httpd.conf. The default document root, where websites are stored, is typically /var/www/html/. Understanding these defaults is crucial for making modifications and ensuring that your custom configurations are applied correctly.
Configuring the Apache Document Root
To configure the Apache document root, you need to modify the httpd.conf file. Open the file in a text editor, and look for the DocumentRoot directive. By default, it’s set to /var/www/html. You can change this to any directory you prefer, but ensure that the Apache user has read access to this directory. After making changes, restart the Apache service to apply them.
| Directive | Description |
|---|---|
DocumentRoot | Sets the directory that Apache looks for content to serve |
| Configures access control and options for the specified directory |
Setting Up Virtual Hosts

Virtual hosts allow you to host multiple websites on a single Apache server, each with its own domain name and document root. To set up a virtual host, create a new configuration file in the /etc/httpd/conf.d/ directory. In this file, specify the VirtualHost directive, followed by the domain name and the document root for the website. This provides a flexible way to manage multiple websites without conflicts.
VirtualHost block is unique and corresponds to a specific domain or IP address to avoid configuration conflicts.
Configuring Apache for SSL/TLS
To enable SSL/TLS encryption for secure communication between the client and server, you need to configure Apache to use SSL certificates. This involves generating a certificate, updating the Apache configuration to include the SSL certificate and key files, and possibly configuring a virtual host for the HTTPS protocol. This step is crucial for securing user data and complying with modern web security standards.
Optimizing Apache Server Performance
Optimizing the Apache server path configuration can significantly impact performance. Techniques include configuring the FollowSymLinks and Options directives to manage how Apache follows symbolic links and handles file system options, optimizing the server’s Timeout and KeepAlive settings to manage connections efficiently, and using tools like mod_pagespeed to optimize website content. By carefully tuning these settings, you can improve the responsiveness and throughput of your web server.
| Directive | Description |
|---|---|
FollowSymLinks | Enables or disables the server from following symbolic links |
Options | Configures file system options for the specified directory |
Timeout | Sets the number of seconds before receives and sends time out |
How do I restart the Apache service after making configuration changes?
+To restart the Apache service, use the command sudo systemctl restart httpd on AlmaLinux. This ensures that the new configurations are applied.
What is the purpose of the DocumentRoot directive in Apache configuration?
+
The DocumentRoot directive specifies the directory that Apache looks for content to serve. It's a crucial setting for defining where your website files are located.
How do I configure Apache to serve multiple websites?
+To serve multiple websites, you can configure virtual hosts. Each virtual host block in your Apache configuration specifies a domain name and a document root, allowing you to host multiple websites on a single server.
In conclusion, configuring the Apache server path on AlmaLinux is a multifaceted process that involves understanding default configurations, setting up document roots, configuring virtual hosts, enabling SSL/TLS encryption, and optimizing server performance. By following these steps and understanding the nuances of Apache configuration, you can set up a robust, secure, and high-performance web server capable of hosting a variety of web applications and websites.
