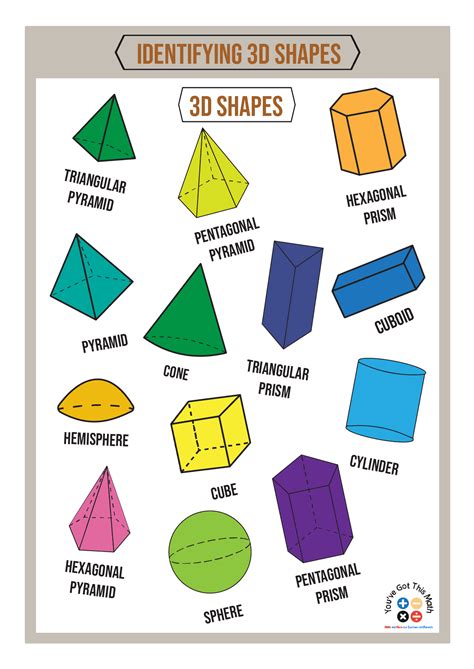
Understanding the fundamental concepts of 3D geometry is crucial for various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design. Among these concepts, 3D shapes are the building blocks that help create complex structures and models. This article will delve into the 7 basic 3D shapes, exploring their characteristics, properties, and applications. The primary shapes include the cube, cuboid, cylinder, sphere, cone, pyramid, and prism. Each of these shapes has unique features and plays a significant role in the world of 3D geometry.
Key Points
- The cube is a 3D shape with 6 equal square faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices, often used in architecture and design for its symmetrical properties.
- The cuboid, or rectangular prism, is characterized by 6 rectangular faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices, commonly found in everyday objects like books and boxes.
- The cylinder is a curved 3D shape with 2 circular bases and a curved lateral surface, used in various applications from pipes to containers.
- The sphere is a perfectly round 3D shape with all points equidistant from its center, appearing in nature and in man-made objects like balls and globes.
- The cone is a 3D shape tapering from a circular base to a point, used in structures like roofs and in applications requiring a funneling effect.
- The pyramid is a polyhedron with a square base and four triangular faces that meet at the apex, famous for ancient structures like the Egyptian pyramids.
- The prism is a 3D shape with two identical faces connected by a band of rectangles, often used in optics and as a basic form in many designs.
Introduction to Basic 3D Shapes
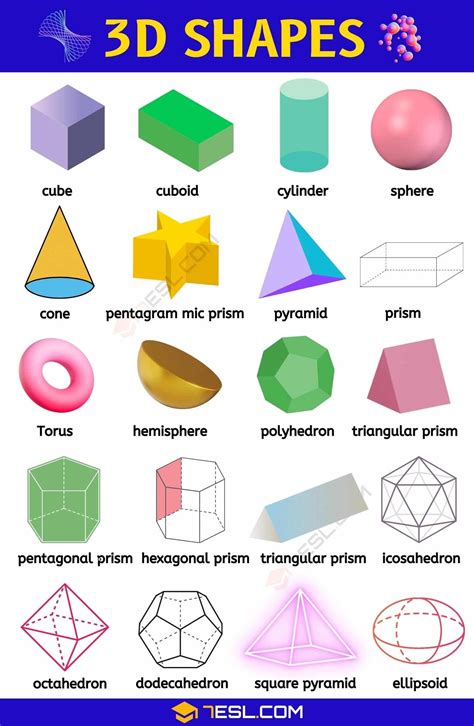
3D shapes, or three-dimensional shapes, are solid objects that have length, width, and depth. Unlike 2D shapes, which can be drawn on a piece of paper, 3D shapes occupy space and can be viewed from different angles. The study of 3D shapes is fundamental in mathematics, science, and engineering, as it provides the foundation for understanding more complex structures and phenomena. The 7 basic 3D shapes are not only the simplest forms but also the components of more intricate shapes and designs.
The Cube
A cube is a special type of cuboid where all the edges have the same length. It has 6 faces, each of which is a square. The cube has 12 edges and 8 vertices. It is a highly symmetrical object, which makes it useful in various applications, including architecture and design. The cube’s properties, such as its equal dimensions and symmetrical faces, contribute to its stability and aesthetic appeal.
The Cuboid (Rectangular Prism)
A cuboid, also known as a rectangular prism, has 6 faces, each of which is a rectangle. Unlike a cube, not all edges of a cuboid have the same length. It also has 12 edges and 8 vertices. Cuboids are common in everyday life, seen in objects like boxes, books, and buildings. The cuboid’s rectangular faces and right angles make it a versatile shape for construction and design.
The Cylinder
A cylinder is a curved 3D shape with two circular bases connected by a curved lateral surface. It has no vertices or edges in the traditional sense but has two bases and a curved surface. Cylinders are used in a wide range of applications, from piping and tubing to containers and machinery. The curved surface of a cylinder provides strength and stability, making it ideal for structures that require resistance to external forces.
The Sphere
A sphere is a perfectly round 3D shape where every point on its surface is equidistant from its center. It has no edges or vertices and is symmetrical about its center. Spheres appear in nature, such as the Earth and the Moon, and are also used in man-made objects like balls and globes. The sphere’s symmetrical and curved surface makes it a unique and efficient shape for enclosing volume.
The Cone
A cone is a 3D shape that tapers from a circular base to a point, called the apex. It has a circular base and a curved lateral surface that narrows to the apex. Cones are used in structures like roofs and in applications requiring a funneling effect, such as in lighting fixtures. The cone’s shape allows it to distribute weight and forces efficiently, making it a practical choice for certain architectural and engineering applications.
The Pyramid
A pyramid is a polyhedron with a square base and four triangular faces that meet at the apex. The most famous pyramids are the ancient Egyptian pyramids, which were built as tombs for pharaohs. Pyramids have a stable base and a pointed top, making them resistant to external forces. The pyramid’s shape, with its broad base and narrowing sides, provides a stable and efficient structure for supporting weight.
The Prism
A prism is a 3D shape with two identical faces connected by a band of rectangles. The two identical faces are called bases, and they can be any polygon, not just a square or rectangle. Prisms are used in optics, as the shape of some lenses and in the design of various objects for their structural and aesthetic properties. The prism’s shape, with its two identical bases and rectangular sides, makes it useful for applications requiring a specific geometric configuration.
| Shape | Number of Faces | Number of Edges | Number of Vertices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cube | 6 | 12 | 8 |
| Cuboid | 6 | 12 | 8 |
| Cylinder | 2 (bases) | 0 (in traditional sense) | 0 (in traditional sense) |
| Sphere | 1 (curved surface) | 0 | 0 |
| Cone | 1 (base) + 1 (curved surface) | 0 (in traditional sense) | 1 (apex) |
| Pyramid | 5 (1 base + 4 triangular faces) | 8 | 5 |
| Prism | Varies (2 bases + number of rectangular faces) | Varies | Varies |
Applications and Implications
The 7 basic 3D shapes have numerous applications across various fields. In architecture, these shapes are used to design buildings, bridges, and other structures. In engineering, they are used to create machines, mechanisms, and electronic devices. The understanding of these shapes is also crucial in art and design, where they are used to create sculptures, models, and other creative works. Furthermore, the study of 3D shapes helps in understanding more complex geometric concepts and their applications in real-world problems.
Future Perspectives
As technology advances, the application of 3D shapes is becoming more sophisticated. With the advent of 3D printing, it is now possible to create complex shapes and structures that were previously difficult or impossible to produce. Additionally, computer-aided design (CAD) software allows for the precise modeling and analysis of 3D shapes, enabling designers and engineers to optimize their designs for better performance and efficiency. The future of 3D geometry holds much promise, with potential applications in fields like medicine, aerospace, and renewable energy.
What are the 7 basic 3D shapes?
+The 7 basic 3D shapes are the cube, cuboid, cylinder, sphere, cone, pyramid, and prism. Each of these shapes has unique properties and applications.
What is the difference between a cube and a cuboid?
+A cube is a special type of cuboid where all the edges have the same length. In a cuboid, not all edges have the same length, resulting in rectangular faces rather than square ones.
What are some real-world applications of 3D shapes?
+3D shapes are used in architecture, engineering, design, and art. They are found in buildings, bridges, machines, and electronic devices. Understanding 3D shapes is also crucial for creating models, sculptures, and other creative works.
How does the study of 3D shapes contribute to technological advancements?
+The study of 3D shapes is fundamental for technological advancements, especially in fields like 3D printing and computer-aided design. Understanding and manipulating 3D shapes enable the creation of complex structures and designs that were previously impossible to produce.
What role do 3D shapes play in everyday life?
+3D shapes are ubiquitous in everyday life, from the buildings we live and work in, to the objects we use, like books, boxes, and balls. Understanding these shapes helps us appreciate the design and engineering that goes into creating the world around us.
How can the knowledge of 3D shapes be applied in problem-solving?
+Knowledge of 3D shapes can be applied in problem-solving by analyzing the geometric properties of objects and structures. This can help in optimizing designs for better performance, stability, and efficiency, and in finding innovative solutions to complex problems.
In conclusion, the 7 basic 3D shapes are fundamental elements in the world of geometry, with each shape having its unique properties and applications. Understanding these shapes is crucial for various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design. As technology continues to evolve, the application of 3D shapes will become even more sophisticated, leading to advancements in multiple sectors. Whether in the natural world, man-made structures, or technological innovations, 3D shapes play a vital role, making their study both fascinating and essential.