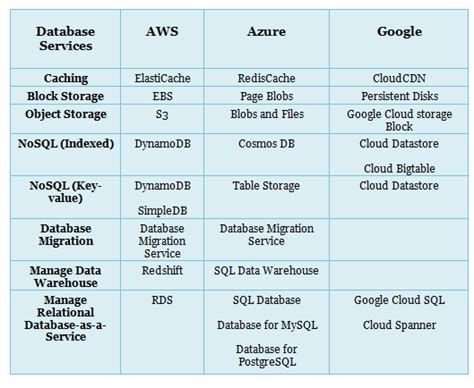
As organizations continue to migrate their operations to the cloud, the role of a Cloud Service Administrator has become increasingly crucial. This professional is responsible for the day-to-day management of cloud services, ensuring that they are secure, efficient, and aligned with the organization's overall IT strategy. To excel in this position, one must be well-versed in a range of key terms and concepts that underpin cloud computing and administration. In this article, we will delve into the foundational terminology that every Cloud Service Administrator should know, providing a comprehensive overview of the cloud ecosystem and the skills required to navigate it effectively.
Key Points
- Understanding of cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) and their applications
- Familiarity with cloud deployment models (public, private, hybrid) and their benefits
- Knowledge of cloud security principles and compliance frameworks
- Ability to manage cloud resources and services efficiently
- Familiarity with cloud migration strategies and post-migration management
Cloud Service Models

Cloud computing is often categorized into three primary service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each model represents a different level of abstraction and management responsibility. IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, allowing for scalability and flexibility in infrastructure management. PaaS offers a complete development and deployment environment for applications, eliminating the need for underlying infrastructure management. SaaS, on the other hand, delivers software applications over the web, reducing the need for local software installation and maintenance. Understanding these models is crucial for Cloud Service Administrators as it helps in selecting the right service model based on organizational needs.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is the most basic cloud service model, where the cloud provider supplies virtualized computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking. This model gives users the highest level of control over the infrastructure but also requires more management effort. Key terms associated with IaaS include virtual machines (VMs), scalability, and elasticity, which refer to the ability to quickly increase or decrease computing resources as needed. IaaS is particularly useful for organizations that require a high degree of customization and control over their infrastructure.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS builds on IaaS by adding a layer of software and tools to support the development, deployment, and management of applications. This model allows developers to focus on application development without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. Important terms in PaaS include runtime environments, frameworks, and libraries, which are essential for application development and deployment. PaaS is beneficial for organizations seeking to streamline their application development processes and reduce the administrative burden associated with infrastructure management.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS provides software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for organizations to install, configure, and maintain software on their premises. Key terms in SaaS include multitenancy, which refers to the model where a single instance of the software serves multiple clients, and automatic updates, which ensures that users always have access to the latest version of the software. SaaS is advantageous for organizations looking to reduce their software maintenance costs and enhance user accessibility.
Cloud Deployment Models
Besides service models, cloud computing can also be classified into different deployment models: public, private, and hybrid. Each model offers distinct advantages and is suited to different organizational needs and security requirements. Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party providers, offering scalability and cost-effectiveness. Private clouds are dedicated to a single organization, providing enhanced security and control. Hybrid clouds combine public and private cloud services, allowing for a more flexible and integrated approach to cloud computing.
Public Cloud
A public cloud is a cloud computing environment that is open for public use, owned by an organization selling cloud services. Key benefits include cost savings, scalability, and reliability. However, public clouds may raise concerns regarding security and compliance, especially for sensitive data. Public clouds are operated by companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Private Cloud
A private cloud, on the other hand, is a cloud environment that is provisioned and managed within a single organization. It offers enhanced security, control, and customization but may require significant upfront investment in infrastructure and maintenance. Private clouds are ideal for organizations with specific security and compliance requirements that cannot be met by public cloud services.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This model provides flexibility, scalability, and cost optimization by leveraging the strengths of both public and private clouds. However, managing a hybrid cloud environment can be complex and requires sophisticated integration and orchestration tools. Hybrid clouds are becoming increasingly popular as they allow organizations to create a cloud strategy that aligns with their business needs.
Cloud Security and Compliance
Security and compliance are critical considerations in cloud computing. Cloud Service Administrators must ensure that cloud services are secure, compliant with relevant laws and regulations, and aligned with organizational security policies. Key terms in cloud security include data encryption, access control, and identity management. Compliance frameworks such as HIPAA for healthcare, PCI-DSS for payment card industry, and GDPR for general data protection are essential for ensuring that cloud services meet legal and regulatory requirements.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is the process of converting plaintext data into unreadable ciphertext to protect it from unauthorized access. In the cloud, data encryption is crucial for ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data both in transit and at rest. Cloud Service Administrators must understand how to implement and manage encryption keys, as well as ensure that data encryption complies with organizational security policies and regulatory requirements.
Access Control
Access control refers to the mechanisms used to grant or deny access to cloud resources based on user identity, role, or other attributes. This includes authentication, which verifies the identity of users, and authorization, which determines what actions users can perform on cloud resources. Cloud Service Administrators must configure access control policies to ensure that cloud services are accessible only to authorized personnel and that access is granted based on the principle of least privilege.
Cloud Resource Management
Effective management of cloud resources is vital for optimizing cloud services, reducing costs, and ensuring compliance with security and regulatory requirements. Cloud Service Administrators must be able to provision and deprovision resources as needed, monitor resource utilization, and optimize resource allocation to match changing business demands. This requires a deep understanding of cloud provider services, pricing models, and best practices for cloud resource management.
Provisioning and Deprovisioning
Provisioning refers to the process of allocating cloud resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networking to support business applications. Deprovisioning involves deallocating resources that are no longer needed to avoid unnecessary costs. Cloud Service Administrators must be able to provision and deprovision resources quickly and efficiently to support agile business operations and to minimize waste.
Cloud Migration and Post-Migration Management
Cloud migration involves moving applications, data, and other business elements from on-premises environments to the cloud. This process requires careful planning, execution, and post-migration management to ensure minimal disruption to business operations. Key terms include assessment, planning, execution, and validation, which are phases of the cloud migration process. Post-migration management involves monitoring cloud services, optimizing resource utilization, and ensuring compliance with security and regulatory requirements.
Assessment and Planning
The assessment phase involves evaluating the readiness of applications and data for cloud migration, identifying potential risks and challenges, and determining the most appropriate cloud service model and deployment strategy. The planning phase involves creating a detailed migration plan, including timelines, resource allocation, and budgeting. Cloud Service Administrators must conduct thorough assessments and develop comprehensive plans to ensure successful cloud migrations.
| Cloud Service Model | Description |
|---|---|
| IaaS | Provides virtualized computing resources |
| PaaS | Offers a development and deployment environment for applications |
| SaaS | Delivers software applications over the web |

Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of a Cloud Service Administrator is multifaceted and demanding, requiring a deep understanding of cloud computing concepts, service models, deployment models, security, compliance, and resource management. By mastering these key terms and concepts, Cloud Service Administrators can effectively manage cloud services, ensure the security and compliance of cloud environments, and contribute to the strategic use of cloud computing within their organizations. As cloud technology continues to evolve, the importance of skilled professionals who can navigate the complexities of cloud services will only continue to grow.
What are the primary cloud service models?
+The primary cloud service models are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each model provides a different level of abstraction and management responsibility, catering to various organizational needs and preferences.
What is the difference between public, private, and hybrid clouds?
+Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party providers, offering scalability and cost-effectiveness. Private clouds are dedicated to a single organization, providing enhanced security and control. Hybrid clouds combine public and private cloud services, allowing for a more flexible and integrated approach to cloud computing.
Why is cloud security important?
+Cloud security is crucial for protecting cloud services from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. This involves implementing various security measures such as data encryption, access control, and identity management to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of cloud resources.
Meta Description: Discover the key terms and concepts that every Cloud Service Administrator should know, from cloud service models and deployment models to cloud security and compliance. Learn how to effectively manage cloud services and ensure the security and compliance of cloud environments.