Content management systems (CMS) have become an integral part of digital landscapes, enabling organizations to create, manage, and deliver content across various platforms. However, the proliferation of different CMS solutions has led to a pressing need for interoperability, allowing seamless communication and data exchange between disparate systems. This is where Content Management Interoperability Services (CMIS) come into play, providing a standardized framework for integrating and managing content across multiple repositories. In this article, we will delve into the world of CMIS, exploring its core principles, benefits, and applications, as well as its potential to simplify content management processes.
Key Points
- CMIS provides a standardized API for accessing and managing content across multiple repositories
- Improves interoperability between different content management systems
- Enhances collaboration and content sharing across organizations
- Supports multiple data models and query languages
- Offers a scalable and flexible architecture for content management
Introduction to CMIS
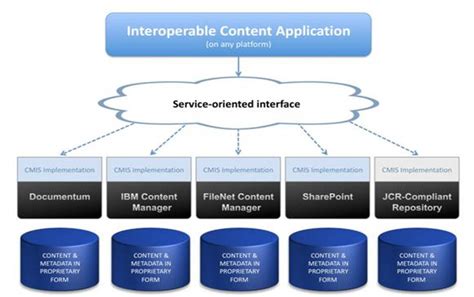
CMIS is an open standard for ECM (Enterprise Content Management) systems, developed by the OASIS (Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards) consortium. The primary goal of CMIS is to provide a common interface for accessing and managing content across different repositories, regardless of the underlying platform or technology. By doing so, CMIS enables organizations to integrate their content management systems, facilitating seamless content sharing, collaboration, and reuse.
Core Principles of CMIS
CMIS is built around several core principles, including:
- Repository abstraction: CMIS provides a standardized interface for accessing and managing content, abstracting the underlying repository’s complexities.
- Service-oriented architecture: CMIS follows a service-oriented architecture, allowing clients to interact with content repositories using a set of standardized services.
- Data model flexibility: CMIS supports multiple data models, enabling clients to work with different types of content and metadata.
- Query language support: CMIS supports multiple query languages, including SQL and XPath, allowing clients to query content repositories using familiar syntax.
| CMIS Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved interoperability | CMIS enables seamless communication between different content management systems |
| Enhanced collaboration | CMIS facilitates content sharing and collaboration across organizations |
| Increased scalability | CMIS supports a scalable and flexible architecture for content management |
| Simplified content management | CMIS provides a standardized interface for accessing and managing content |
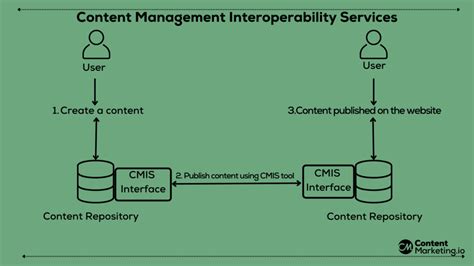
CMIS Applications and Use Cases
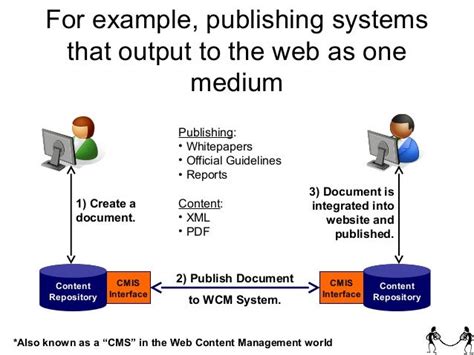
CMIS has a wide range of applications and use cases, including:
- Content aggregation: CMIS enables organizations to aggregate content from multiple repositories, creating a unified view of their content assets.
- Content sharing: CMIS facilitates content sharing and collaboration across organizations, improving knowledge management and reducing content duplication.
- Content migration: CMIS provides a standardized interface for migrating content between different repositories, reducing the complexity and cost of content migration projects.
- Content analytics: CMIS enables organizations to analyze content usage and performance across multiple repositories, providing valuable insights into content effectiveness.
CMIS Implementation and Best Practices
Implementing CMIS requires careful planning and consideration of several factors, including:
- Repository selection: Organizations must select a CMIS-compliant repository that meets their content management needs.
- Client development: Organizations must develop CMIS clients that can interact with the selected repository.
- Content modeling: Organizations must define a content model that aligns with their business requirements and CMIS data models.
- Security and authentication: Organizations must implement robust security and authentication mechanisms to protect their content and ensure authorized access.
By following these best practices and considering the benefits and applications of CMIS, organizations can simplify their content management processes, improve collaboration and content sharing, and reduce the complexity and cost of content management.
What is CMIS and how does it work?
+CMIS is an open standard for ECM systems that provides a standardized interface for accessing and managing content across different repositories. It works by abstracting the underlying repository’s complexities and providing a service-oriented architecture for clients to interact with content repositories.
What are the benefits of using CMIS?
+The benefits of using CMIS include improved interoperability, enhanced collaboration, increased scalability, and simplified content management. CMIS enables organizations to break down content silos and improve content sharing and reuse.
How do I implement CMIS in my organization?
+To implement CMIS in your organization, you must select a CMIS-compliant repository, develop CMIS clients, define a content model, and implement robust security and authentication mechanisms. It is also essential to consider factors such as repository selection, client development, content modeling, and security and authentication.