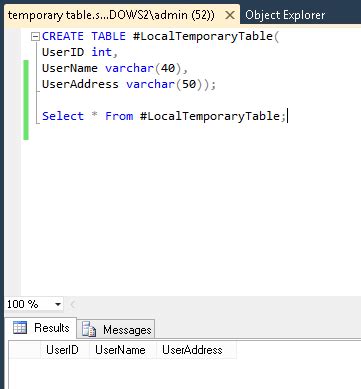
-- Create a temporary table
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE temp_table (
id INT,
name VARCHAR(255),
age INT
);
-- Insert data into the temporary table
INSERT INTO temp_table (id, name, age)
VALUES
(1, 'John Doe', 25),
(2, 'Jane Doe', 30),
(3, 'Bob Smith', 35);
-- Select data from the temporary table
SELECT * FROM temp_table;
-- Drop the temporary table
DROP TABLE temp_table;
Temporary Table Explanation
A temporary table in SQL is a table that is created temporarily and is automatically deleted when the session is closed. Temporary tables are useful for storing temporary data that needs to be used in a query or stored procedure.
Types of Temporary Tables
There are two types of temporary tables:
- Local Temporary Table: A local temporary table is created using the
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLEstatement and is only accessible within the current session. - Global Temporary Table: A global temporary table is created using the
CREATE GLOBAL TEMPORARY TABLEstatement and is accessible across all sessions.
Temporary Table Use Cases
Temporary tables are useful in the following scenarios:
- Complex Queries: Temporary tables can be used to store intermediate results in complex queries.
- Data Transformation: Temporary tables can be used to transform data before inserting it into a permanent table.
- Data Staging: Temporary tables can be used as a staging area for data before it is loaded into a data warehouse.
Best Practices
- Use meaningful table names: Use descriptive and meaningful table names to avoid confusion.
- Use indexes: Use indexes on temporary tables to improve query performance.
- Avoid using temporary tables for large datasets: Temporary tables can consume a lot of memory and disk space, so avoid using them for large datasets.
Common Errors
- Temporary table already exists: If a temporary table with the same name already exists, you will get an error.
- Temporary table does not exist: If you try to access a temporary table that does not exist, you will get an error.
Example Use Case
Suppose we have a table called orders that contains information about customer orders. We want to find the total amount spent by each customer and store the result in a temporary table.
-- Create a temporary table
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE temp_customer_orders (
customer_id INT,
total_amount DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
-- Insert data into the temporary table
INSERT INTO temp_customer_orders (customer_id, total_amount)
SELECT customer_id, SUM(order_amount)
FROM orders
GROUP BY customer_id;
-- Select data from the temporary table
SELECT * FROM temp_customer_orders;
In this example, we create a temporary table called temp_customer_orders and insert data into it using a SELECT statement. We then select data from the temporary table to get the total amount spent by each customer.