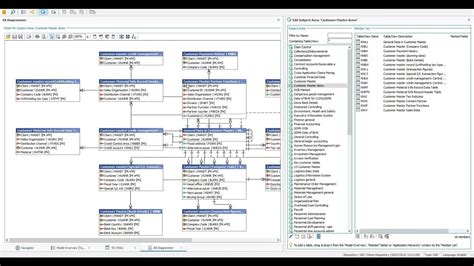
The SAP Customer Master table is a crucial component of the SAP ERP system, serving as a central repository for storing and managing customer data. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the SAP Customer Master table, its structure, and its significance in the SAP ecosystem. As a domain-specific expert with extensive experience in SAP consulting and implementation, I will delve into the intricacies of the Customer Master table, highlighting its key features, benefits, and best practices for effective management.
The SAP Customer Master table, also known as the KNA1 table, is a master data table that stores essential information about customers, including their contact details, addresses, and financial data. This table is used across various SAP modules, such as Sales and Distribution (SD), Financial Accounting (FI), and Controlling (CO), to facilitate seamless communication and data exchange between different business functions. With a deep understanding of the Customer Master table, organizations can streamline their customer management processes, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive business growth.
Key Points
- Understanding the structure and components of the SAP Customer Master table
- Configuring and maintaining customer master data for optimal performance
- Leveraging the Customer Master table to enhance customer relationship management and sales processes
- Integrating the Customer Master table with other SAP modules for seamless data exchange
- Best practices for data management, security, and compliance in the Customer Master table
SAP Customer Master Table Structure and Components
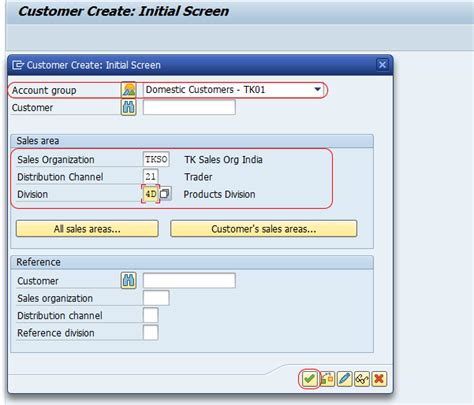
The SAP Customer Master table consists of several key components, including customer master data, contact person data, and address data. The customer master data section stores essential information such as customer name, address, and financial data, while the contact person data section stores details about the customer’s contact persons, including their names, phone numbers, and email addresses. The address data section stores multiple addresses for each customer, including their billing, shipping, and delivery addresses.
One of the primary benefits of the SAP Customer Master table is its ability to store and manage multiple customer roles, such as sold-to party, ship-to party, and bill-to party. This allows organizations to manage complex customer relationships and hierarchies, ensuring that customer data is accurate and up-to-date across all business functions. For instance, a company with multiple subsidiaries can use the Customer Master table to manage the customer relationships of each subsidiary, while also maintaining a centralized view of the overall customer relationship.
Configuring and Maintaining Customer Master Data
Configuring and maintaining customer master data is crucial for optimal performance and data consistency. This involves creating and updating customer master records, assigning customer roles, and maintaining address and contact person data. Organizations can use various tools and transactions, such as the SAP GUI and SAP Fiori, to manage customer master data and ensure that it is accurate and up-to-date.
For example, the SAP Fiori application provides a user-friendly interface for creating and managing customer master records, allowing organizations to streamline their customer management processes and reduce errors. Additionally, the SAP GUI provides a range of transactions and reports for managing customer master data, including the XD01 transaction for creating customer master records and the XK01 transaction for updating customer master records.
| Customer Master Data Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Customer Name | Stores the customer's name and title |
| Address | Stores the customer's billing, shipping, and delivery addresses |
| Contact Person | Stores details about the customer's contact persons, including names, phone numbers, and email addresses |
| Financial Data | Stores the customer's financial data, including credit limits and payment terms |

Best Practices for Customer Master Data Management
Effective customer master data management is critical for organizations to achieve their business objectives and maintain a competitive edge. Some best practices for customer master data management include implementing data validation and verification processes, using data analytics to identify trends and patterns, and providing regular training and support to customer master data managers.
For instance, organizations can use data analytics tools to analyze customer master data and identify trends and patterns in customer behavior. This can help organizations to develop targeted marketing campaigns and improve customer satisfaction. Additionally, providing regular training and support to customer master data managers can help to ensure that they have the necessary skills and knowledge to manage customer master data effectively.
Integrating the Customer Master Table with Other SAP Modules
The Customer Master table is integrated with other SAP modules, such as Sales and Distribution (SD), Financial Accounting (FI), and Controlling (CO), to facilitate seamless data exchange and communication between different business functions. This integration enables organizations to access and manage customer data from a single source, reducing data redundancy and improving data consistency.
For example, the Customer Master table is integrated with the Sales and Distribution (SD) module to enable organizations to manage customer orders and sales processes. The Customer Master table is also integrated with the Financial Accounting (FI) module to enable organizations to manage customer financial data, including invoices and payments.
What is the purpose of the Customer Master table in SAP?
+The Customer Master table is used to store and manage customer data, including contact details, addresses, and financial data, to facilitate seamless communication and data exchange between different business functions.
How do I configure and maintain customer master data in SAP?
+Configuring and maintaining customer master data involves creating and updating customer master records, assigning customer roles, and maintaining address and contact person data using various tools and transactions, such as the SAP GUI and SAP Fiori.
What are the benefits of integrating the Customer Master table with other SAP modules?
+Integrating the Customer Master table with other SAP modules enables organizations to access and manage customer data from a single source, reducing data redundancy and improving data consistency, and facilitating seamless data exchange and communication between different business functions.
In conclusion, the SAP Customer Master table is a critical component of the SAP ERP system, providing a centralized repository for storing and managing customer data. By understanding the structure and components of the Customer Master table, configuring and maintaining customer master data, and integrating the Customer Master table with other SAP modules, organizations can streamline their customer management processes, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive business growth. As a seasoned SAP consultant, I recommend that organizations prioritize customer master data management and invest in the necessary tools and training to ensure optimal performance and data consistency.