The world of data management is constantly evolving, with new technologies and architectures emerging to help organizations better store, process, and analyze their data. Two popular concepts that have gained significant attention in recent years are Data Mesh and Data Lake. While both are designed to manage large volumes of data, they differ fundamentally in their approach, architecture, and use cases. In this article, we will delve into the details of Data Mesh and Data Lake, exploring their key characteristics, advantages, and limitations, as well as the scenarios in which one might be preferred over the other.
Key Points
- Data Mesh is a decentralized data architecture that treats data as a product, emphasizing domain-oriented, self-service, and federated governance.
- Data Lake is a centralized repository that stores raw, unprocessed data in its native format, allowing for flexible schema-on-read analytics.
- Data Mesh focuses on data quality, accessibility, and usability, whereas Data Lake prioritizes data storage, scalability, and flexibility.
- Data Mesh is suitable for organizations with complex, domain-specific data needs, while Data Lake is ideal for those requiring massive data storage and processing capabilities.
- Both Data Mesh and Data Lake require careful planning, governance, and management to ensure their successful implementation and operation.
Data Mesh: A Decentralized Data Architecture

Data Mesh is a relatively new concept that has gained popularity in recent years, especially among organizations with complex, domain-specific data needs. It is a decentralized data architecture that treats data as a product, with a focus on domain-oriented, self-service, and federated governance. In a Data Mesh, data is owned and managed by the respective business domains, which are responsible for ensuring its quality, accessibility, and usability.
The key characteristics of a Data Mesh include:
- Domain-oriented data ownership: Data is owned and managed by the respective business domains, ensuring that data is accurate, complete, and consistent.
- Self-service data infrastructure: Data consumers can access and use data without relying on a centralized IT team, promoting agility and flexibility.
- Federated governance: Governance is distributed across multiple domains, ensuring that data is managed consistently and in accordance with organizational policies.
Data Mesh offers several advantages, including improved data quality, increased data accessibility, and enhanced data usability. However, it also presents challenges, such as ensuring data consistency, managing data complexity, and maintaining federated governance.
Benefits and Challenges of Data Mesh
The benefits of Data Mesh include:
- Improved data quality: Data is owned and managed by the respective business domains, ensuring that data is accurate, complete, and consistent.
- Increased data accessibility: Data consumers can access and use data without relying on a centralized IT team, promoting agility and flexibility.
- Enhanced data usability: Data is presented in a consistent and standardized format, making it easier for data consumers to understand and use.
However, Data Mesh also presents challenges, such as:
- Ensuring data consistency: With data owned and managed by multiple domains, ensuring data consistency and accuracy can be a challenge.
- Managing data complexity: Data Mesh can introduce additional complexity, requiring careful planning and management to ensure its successful implementation and operation.
- Maintaining federated governance: Federated governance can be challenging to establish and maintain, requiring careful coordination and communication across multiple domains.
Data Lake: A Centralized Repository for Raw Data
Data Lake is a centralized repository that stores raw, unprocessed data in its native format, allowing for flexible schema-on-read analytics. It is designed to handle massive volumes of data, providing a scalable and flexible solution for data storage and processing. In a Data Lake, data is stored in a centralized location, and data consumers can access and analyze the data as needed.
The key characteristics of a Data Lake include:
- Centralized data storage: Data is stored in a centralized location, providing a single source of truth for data.
- Raw, unprocessed data: Data is stored in its native format, without any processing or transformation.
- Flexible schema-on-read analytics: Data consumers can define the schema and analyze the data as needed, providing flexibility and agility.
Data Lake offers several advantages, including massive data storage and processing capabilities, flexible schema-on-read analytics, and cost-effective data storage. However, it also presents challenges, such as ensuring data quality, managing data complexity, and maintaining data governance.
Benefits and Challenges of Data Lake
The benefits of Data Lake include:
- Massive data storage and processing capabilities: Data Lake can handle massive volumes of data, providing a scalable solution for data storage and processing.
- Flexible schema-on-read analytics: Data consumers can define the schema and analyze the data as needed, providing flexibility and agility.
- Cost-effective data storage: Data Lake can provide a cost-effective solution for data storage, especially for large volumes of data.
However, Data Lake also presents challenges, such as:
- Ensuring data quality: With data stored in its raw, unprocessed form, ensuring data quality and accuracy can be a challenge.
- Managing data complexity: Data Lake can introduce additional complexity, requiring careful planning and management to ensure its successful implementation and operation.
- Maintaining data governance: Data governance can be challenging to establish and maintain, requiring careful coordination and communication across multiple stakeholders.
| Characteristics | Data Mesh | Data Lake |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Domain-oriented | Centralized |
| Data Storage | Decentralized | Centralized |
| Data Processing | Self-service | Flexible schema-on-read |
| Governance | Federated | Centralized |
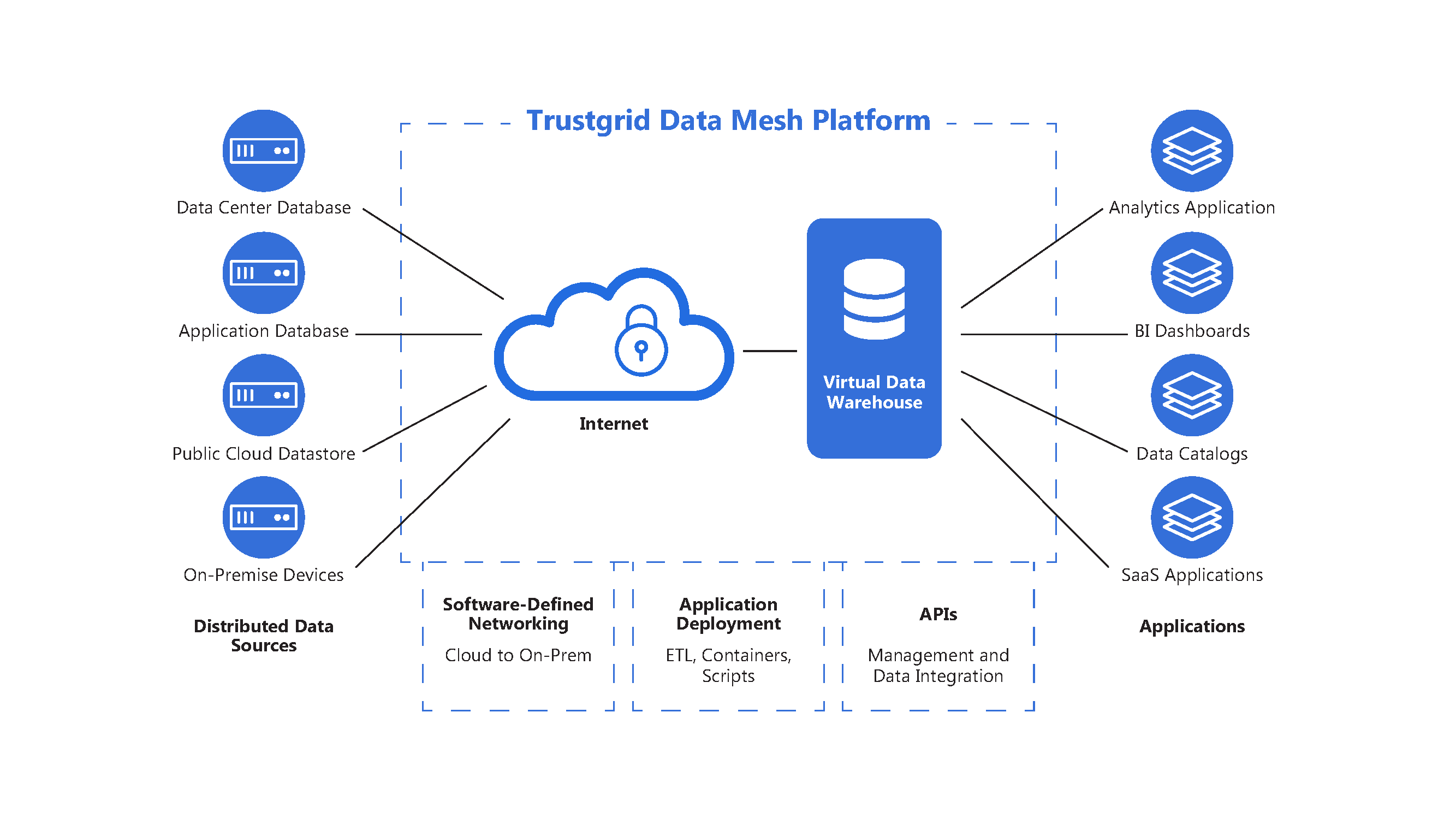
In conclusion, Data Mesh and Data Lake are two distinct approaches to data management, each with its strengths and weaknesses. By understanding the key characteristics, advantages, and limitations of each approach, organizations can make informed decisions about which one to adopt, or whether to combine elements of both to create a hybrid solution. Regardless of the approach chosen, careful planning, governance, and management are essential to ensure the successful implementation and operation of a data management system.
What is the primary difference between Data Mesh and Data Lake?
+The primary difference between Data Mesh and Data Lake is their approach to data management. Data Mesh is a decentralized data architecture that treats data as a product, while Data Lake is a centralized repository that stores raw, unprocessed data in its native format.
Which approach is suitable for organizations with complex, domain-specific data needs?
+Data Mesh is suitable for organizations with complex, domain-specific data needs, as it provides a decentralized data architecture that allows for domain-oriented data ownership and self-service data infrastructure.
What are the benefits of using a Data Lake?
+The benefits of using a Data Lake include massive data storage and processing capabilities, flexible schema-on-read analytics, and cost-effective data storage.