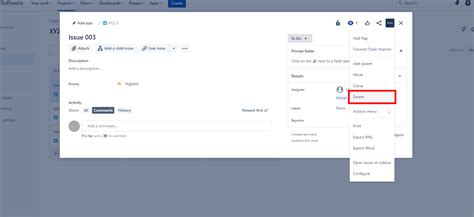
Managing user accounts is a crucial aspect of system administration, ensuring that access is properly controlled and that security is maintained. Removing users, whether due to termination of employment, contract expiration, or security concerns, is a key part of this process. There are several methods to remove users from a system, each with its own set of considerations and implications. In this article, we will explore five ways to remove users, discussing the steps involved, the scenarios in which each method is most appropriate, and the potential impacts on the system and its remaining users.
Understanding User Removal
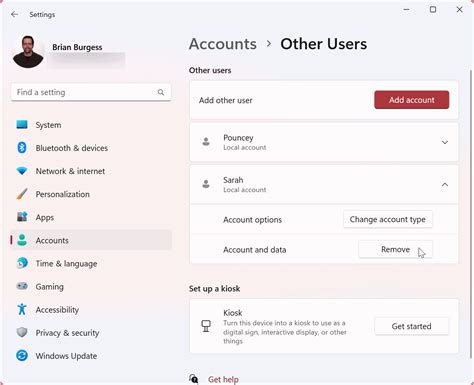
Before diving into the methods of removing users, it’s essential to understand the reasons behind this action. User removal is not just about deleting an account; it involves considering the implications on data integrity, system security, and compliance with organizational policies. Each method of user removal has its specific use cases, ranging from temporary account suspensions to permanent deletions, and the choice of method depends on the reason for removal and the system’s requirements.
Key Points
- Permanent deletion of a user account is a irreversible action that should be taken with caution.
- Temporary suspension can be a more flexible approach, allowing for the potential reinstatement of the user.
- Disabling a user account can be a preliminary step before permanent deletion, allowing for a grace period.
- Renaming or reassigning a user account can be an effective way to manage role changes within an organization.
- Exporting user data before removal can be crucial for compliance and auditing purposes.
Method 1: Permanent Deletion
Permanent deletion involves completely removing a user’s account from the system, including all associated data and permissions. This method is typically used when a user is leaving an organization permanently, or when an account has been compromised and cannot be recovered. The steps for permanent deletion vary by system but generally involve selecting the user account, confirming the action, and then deleting the account. It’s crucial to ensure that all necessary data is backed up or transferred before deletion, as this action is irreversible.
| System | Deletion Steps |
|---|---|
| Windows | 1. Open Computer Management, 2. Navigate to Local Users and Groups, 3. Select the user, 4. Click Delete. |
| Linux | 1. Open Terminal, 2. Use the command "userdel [username]" followed by "yes" to confirm. |
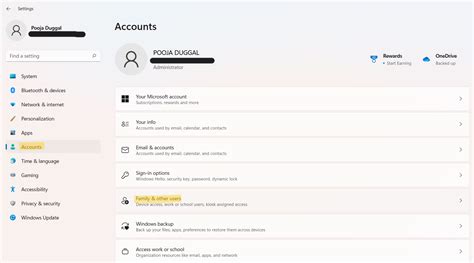
Method 2: Temporary Suspension
Suspending a user account temporarily restricts access without deleting the account or its data. This method is useful for situations where access needs to be revoked for a period, such as during an investigation or when a user is on leave. To suspend an account, administrators typically access the user management interface, select the account, and apply a suspension or lockout status. The specifics can vary significantly between systems, but the principle remains the same: to temporarily deny access without permanent deletion.
Method 3: Disabling a User Account
Disabling a user account is a step that can precede permanent deletion, especially in scenarios where there’s a need to immediately stop a user’s access but the decision for permanent removal hasn’t been finalized. Disabling an account typically involves changing the account’s status to inactive or disabled, which prevents login but keeps the account and its associated data intact. This method allows for a grace period during which the decision for permanent deletion can be reconsidered or the account can be re-enabled if necessary.
Method 4: Renaming or Reassigning a User Account
In some cases, rather than removing a user, it’s more appropriate to rename or reassign the user account. This can happen when job roles change within an organization, and the existing account’s permissions and access rights are still relevant but need to be associated with a different user. Renaming involves updating the account’s username and other identifying information, while reassigning involves transferring the account’s ownership and permissions to another user. Both methods require careful consideration of security and access control implications.
Method 5: Exporting User Data Before Removal
Before permanently removing a user account, it’s often necessary to export the associated data for archival, compliance, or auditing purposes. This can include emails, documents, and other files associated with the user. The process of exporting user data varies significantly depending on the system and the types of data involved. It’s crucial to ensure that the data export is handled securely and in accordance with relevant data protection regulations to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
What is the difference between suspending and disabling a user account?
+Suspending an account typically implies a temporary restriction of access due to a specific reason such as security concerns or policy violations, while disabling is often a more administrative action that can precede permanent deletion or is used for accounts that are not currently in use but may be needed in the future.
How do I ensure compliance with data protection regulations when removing user accounts?
+Ensuring compliance involves following the organization's data retention and deletion policies, exporting data securely when necessary, and documenting all actions taken during the removal process. It's also crucial to be aware of and adhere to relevant external regulations such as GDPR or CCPA.
In conclusion, removing users from a system is a critical administrative task that requires careful consideration of the method used, the potential impacts on the system and its users, and adherence to organizational policies and external regulations. By understanding the different methods available and their appropriate use cases, system administrators can ensure that user removal is handled efficiently, securely, and in compliance with all relevant standards.