Setting a primary key in Microsoft Access is a crucial step in designing a robust and efficient database. A primary key is a unique identifier for each record in a table, ensuring that no two records have the same value. This helps maintain data integrity, prevents data duplication, and enables efficient data retrieval. In this article, we will delve into the world of primary keys, exploring their importance, types, and the step-by-step process of setting a primary key in Access.
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of primary keys and their significance in database design
- Learning how to set a primary key in Access, including the use of a single field or a combination of fields
- Exploring the types of primary keys, including auto-number fields and user-defined keys
- Discovering how to modify or delete a primary key, and understanding the implications of these actions
- Best practices for choosing the right field(s) to serve as the primary key
Understanding Primary Keys

A primary key is a field or set of fields that uniquely identifies each record in a table. It serves as a unique identifier, ensuring that no two records have the same value. Primary keys play a crucial role in maintaining data integrity, preventing data duplication, and enabling efficient data retrieval. When designing a database, it’s essential to choose the right field(s) to serve as the primary key, taking into account factors such as uniqueness, stability, and simplicity.
Types of Primary Keys
There are two main types of primary keys: auto-number fields and user-defined keys. Auto-number fields are automatically generated by Access, providing a unique identifier for each record. User-defined keys, on the other hand, are created by the user, using a combination of fields to uniquely identify each record. Both types of primary keys have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which one to use depends on the specific requirements of the database.
Setting a Primary Key in Access

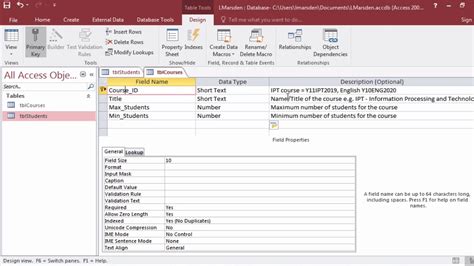
Setting a primary key in Access is a straightforward process that can be accomplished in a few steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Open the table in Design View by right-clicking on the table and selecting "Design View" from the context menu.
- Select the field(s) you want to use as the primary key by clicking on the field name in the "Field Name" column.
- Click on the "Primary Key" button in the "Tools" group on the "Design" tab of the ribbon.
- Alternatively, you can right-click on the selected field(s) and choose "Primary Key" from the context menu.
- Access will display a prompt asking you to confirm that you want to set the selected field(s) as the primary key. Click "Yes" to proceed.
Modifying or Deleting a Primary Key
Modifying or deleting a primary key can have significant implications for the database, and should be done with caution. To modify a primary key, you can follow the same steps as setting a primary key, selecting the new field(s) you want to use. To delete a primary key, you can click on the “Primary Key” button again, or right-click on the field(s) and choose “Primary Key” from the context menu. Access will prompt you to confirm that you want to delete the primary key, and you should exercise caution before proceeding.
| Primary Key Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Auto-Number Field | Automatically generated by Access, providing a unique identifier for each record |
| User-Defined Key | Created by the user, using a combination of fields to uniquely identify each record |

Best Practices for Choosing a Primary Key
Choosing the right field(s) to serve as the primary key is crucial for the success of the database. Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Choose a field that is unique and stable, meaning it won't change frequently.
- Avoid using fields that can be null or empty, as this can lead to data inconsistencies.
- Consider using a combination of fields to create a composite primary key, especially if no single field can uniquely identify each record.
- Use auto-number fields when possible, as they provide a convenient and efficient way to generate unique identifiers.
What is the purpose of a primary key in a database?
+A primary key serves as a unique identifier for each record in a table, ensuring that no two records have the same value. It helps maintain data integrity, prevents data duplication, and enables efficient data retrieval.
How do I set a primary key in Access?
+To set a primary key in Access, open the table in Design View, select the field(s) you want to use as the primary key, and click on the "Primary Key" button in the "Tools" group on the "Design" tab of the ribbon.
Can I modify or delete a primary key in Access?
+Yes, you can modify or delete a primary key in Access, but this should be done with caution. Modifying or deleting a primary key can have significant implications for the database, and you should exercise caution before proceeding.
Meta Description: Learn how to set a primary key in Microsoft Access, including the importance of primary keys, types of primary keys, and step-by-step instructions for setting a primary key. Discover best practices for choosing the right field(s) to serve as the primary key and how to modify or delete a primary key.