The American Heart Association's (AHA) Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) system is a comprehensive framework designed to improve outcomes for adult patients with cardiac arrest or other life-threatening cardiovascular conditions. The ACLS system is built around six key elements, which are crucial for providing high-quality care to patients in cardiac arrest. These elements work together to ensure that patients receive the best possible chance of survival and optimal outcomes.
Introduction to ACLS System Elements
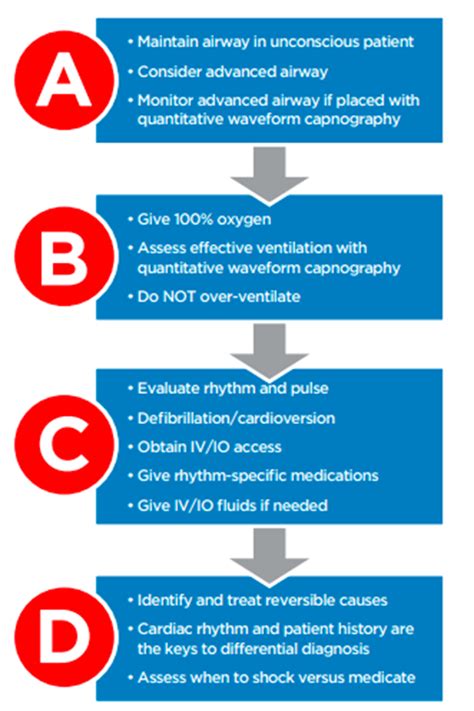
The six elements of the ACLS system are: (1) High-Quality CPR, (2) Airway Management, (3) Rhythm Recognition, (4) Defibrillation and Cardioversion, (5) Medication Administration, and (6) Post-Cardiac Arrest Care. Each element plays a vital role in the management of cardiac arrest, and together they form a cohesive system that guides healthcare providers in their response to these critical situations.
Key Points
- The ACLS system is based on six key elements that work together to improve patient outcomes.
- High-Quality CPR is the foundation of the ACLS system, emphasizing the importance of proper chest compression and ventilation techniques.
- Airway Management is critical for ensuring adequate oxygenation and ventilation of the patient.
- Rhythm Recognition is essential for guiding the management of cardiac arrest, including the administration of medications and the use of defibrillation and cardioversion.
- Defibrillation and Cardioversion are critical interventions for managing life-threatening arrhythmias.
- Medication Administration and Post-Cardiac Arrest Care are also vital components of the ACLS system, focusing on the use of evidence-based medications and the provision of comprehensive care after the return of spontaneous circulation.
Element 1: High-Quality CPR
High-Quality CPR is the foundation of the ACLS system, emphasizing the importance of proper chest compression and ventilation techniques. This element focuses on providing CPR that meets specific guidelines, including a compression rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute, a compression depth of at least 2 inches, and a ventilation rate of 8 to 12 breaths per minute. High-Quality CPR is critical for maintaining perfusion of vital organs during cardiac arrest, and its quality is directly linked to patient outcomes.
Importance of High-Quality CPR
The importance of High-Quality CPR cannot be overstated. Studies have shown that the quality of CPR is directly correlated with patient outcomes, including survival and neurological function. For example, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that patients who received High-Quality CPR had a significantly higher likelihood of survival and good neurological function compared to those who received standard CPR.
Element 2: Airway Management
Airway Management is critical for ensuring adequate oxygenation and ventilation of the patient. This element involves the use of advanced airway devices, such as endotracheal tubes and laryngeal mask airways, to secure the patient’s airway and provide adequate ventilation. Airway Management is essential for preventing complications, such as aspiration and hypoxia, and for ensuring that the patient receives adequate oxygenation and ventilation during cardiac arrest.
Techniques for Airway Management
There are several techniques for Airway Management, including bag-valve-mask ventilation, endotracheal intubation, and laryngeal mask airway insertion. Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technique depends on the patient’s specific needs and the provider’s level of expertise. For example, endotracheal intubation is generally considered the gold standard for Airway Management, but it requires a high level of skill and expertise to perform correctly.
Element 3: Rhythm Recognition
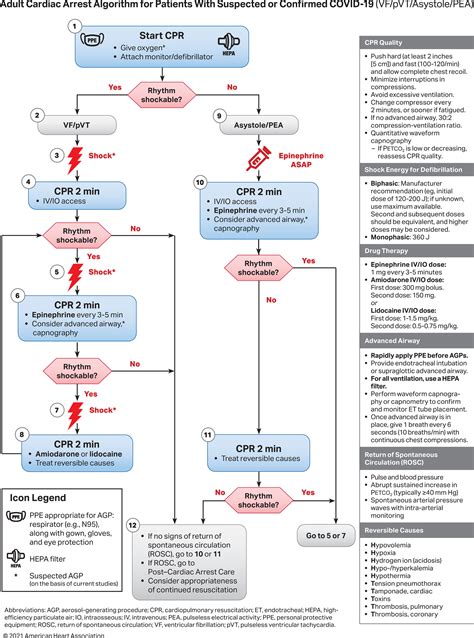
Rhythm Recognition is essential for guiding the management of cardiac arrest, including the administration of medications and the use of defibrillation and cardioversion. This element involves the use of electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring to identify the patient’s cardiac rhythm and guide treatment. Rhythm Recognition is critical for distinguishing between shockable and non-shockable rhythms, and for guiding the administration of evidence-based medications.
Common Cardiac Rhythms
There are several common cardiac rhythms that are encountered during cardiac arrest, including ventricular fibrillation, pulseless ventricular tachycardia, and asystole. Each rhythm has its own specific treatment strategy, and Rhythm Recognition is essential for guiding treatment and improving patient outcomes. For example, ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia are shockable rhythms that require immediate defibrillation, while asystole is a non-shockable rhythm that requires the administration of epinephrine and other medications.
Element 4: Defibrillation and Cardioversion
Defibrillation and Cardioversion are critical interventions for managing life-threatening arrhythmias. Defibrillation involves the use of electrical shocks to convert a shockable rhythm, such as ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia, to a perfusing rhythm. Cardioversion involves the use of electrical shocks to convert a non-shockable rhythm, such as atrial fibrillation or supraventricular tachycardia, to a perfusing rhythm. Defibrillation and Cardioversion are essential for improving patient outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
Techniques for Defibrillation and Cardioversion
There are several techniques for Defibrillation and Cardioversion, including manual defibrillation, automated external defibrillation, and cardioversion using a biphasic defibrillator. Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technique depends on the patient’s specific needs and the provider’s level of expertise. For example, manual defibrillation requires a high level of skill and expertise, while automated external defibrillation is generally easier to use and requires less training.
Element 5: Medication Administration
Medication Administration is a critical component of the ACLS system, focusing on the use of evidence-based medications to manage cardiac arrest and other life-threatening conditions. This element involves the administration of medications, such as epinephrine, atropine, and amiodarone, to guide treatment and improve patient outcomes. Medication Administration is essential for managing cardiac arrest, and its quality is directly linked to patient outcomes.
Common Medications Used in ACLS
There are several common medications used in ACLS, including epinephrine, atropine, and amiodarone. Each medication has its own specific indications and contraindications, and the choice of medication depends on the patient’s specific needs and the provider’s level of expertise. For example, epinephrine is generally used as a first-line medication for cardiac arrest, while atropine is used to manage bradycardia and amiodarone is used to manage tachyarrhythmias.
Element 6: Post-Cardiac Arrest Care
Post-Cardiac Arrest Care is a critical component of the ACLS system, focusing on the provision of comprehensive care after the return of spontaneous circulation. This element involves the management of complications, such as hypoxia and hypotension, and the provision of supportive care, such as mechanical ventilation and vasopressor support. Post-Cardiac Arrest Care is essential for improving patient outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
Importance of Post-Cardiac Arrest Care
The importance of Post-Cardiac Arrest Care cannot be overstated. Studies have shown that the quality of Post-Cardiac Arrest Care is directly correlated with patient outcomes, including survival and neurological function. For example, a study published in the Critical Care Medicine journal found that patients who received high-quality Post-Cardiac Arrest Care had a significantly higher likelihood of survival and good neurological function compared to those who received standard care.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. High-Quality CPR | Proper chest compression and ventilation techniques |
| 2. Airway Management | Use of advanced airway devices to secure the patient's airway |
| 3. Rhythm Recognition | Use of ECG monitoring to identify the patient's cardiac rhythm |
| 4. Defibrillation and Cardioversion | Use of electrical shocks to convert life-threatening arrhythmias |
| 5. Medication Administration | Use of evidence-based medications to manage cardiac arrest |
| 6. Post-Cardiac Arrest Care | Provision of comprehensive care after the return of spontaneous circulation |

What is the purpose of the ACLS system?
+The purpose of the ACLS system is to provide a comprehensive framework for managing cardiac arrest and other life-threatening conditions, with the goal of improving patient outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
What are the six elements of the ACLS system?
+The six elements of the ACLS system are: (1) High-Quality CPR, (2) Airway Management, (3) Rhythm Recognition, (4) Defibrillation and Cardioversion, (5) Medication Administration, and (6) Post-Cardiac Arrest Care.
Why is High-Quality CPR important?
+High-Quality CPR is important because it is directly linked to patient outcomes, including survival and neurological function. Proper chest compression and ventilation techniques are essential for maintaining perfusion of vital organs during cardiac arrest.
In conclusion, the six elements of the ACLS system work together to provide a comprehensive framework for managing cardiac arrest and other life-threatening conditions. By understanding and applying these elements, healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes and reduce the risk of complications. The importance of each element cannot be overstated, and it is essential for healthcare providers to be proficient in all six elements to provide high-quality care to patients in cardiac arrest.